In today’s world, where sustainability and clean energy hold utmost importance, the United Kingdom’s Solar Market has secured its unique position. As of 2023, the UK boasts a total solar capacity of 15 GW, as reported by Solar Energy UK. Notably, this capacity is on an upward trajectory, with 0.952 GW of solar PV capacity being installed between June 2022 and June 2023 alone. Yet, the prominent signs within the UK solar market indicate a loftier goal: achieving a cumulative deployment of 40 GW by the start of 2030.
Let’s explore this industry analysis to uncover valuable insights, understand the factors influencing the market, delve into the residential and commercial segments, and much more!
How many solar panels are there in the UK?
Recent data from the Microgeneration Certification Scheme (MCS) indicates approximately 1.3 million UK households have embraced solar panel installations. Of the 29 million homes in the UK, 4.1% are generating electricity from solar panels. It’s anticipated that this figure will rise as solar panel costs become more budget-friendly.
Commercial solar PV is poised to become a mainstream energy source for businesses of all sizes. Additionally, the UK currently hosts slightly over 1,000 solar farms, contributing clean energy to the national grid.
Factors Influencing the UK Solar Market

The UK solar market forecast for 2022-2027 anticipates robust growth, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) exceeding 5%. However, before this period, the UK encountered challenges, including a sharp drop in domestic demand and a temporary industrial pause in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This downturn notably affected solar panel manufacturers during the first quarter of 2020 compared to the previous year.
Fortunately, the solar market rebounded, driven by government incentives and cost-effective solar components. Nevertheless, the UK solar sector faces ongoing challenges. Land constraints and increasing demand for alternative renewable energy sources may hinder growth.
The UK relies heavily on Asian suppliers for solar components, exposing it to price fluctuations and supply chain vulnerabilities. China, responsible for over 90% of global production, exerts substantial influence. The UK now competes globally to secure solar modules from China and Southeast Asia, posing challenges for gigawatt-plus portfolio expansions.
Intense competition for modules may impact global utilities and corporations striving to meet net-zero and corporate targets in the coming years. While UK solar contributes to global PV demand, it grapples with external forces. The era of buying power based on project size or contracted module volumes has passed, making it a seller’s market.
In this landscape, navigating the UK solar industry necessitates adaptability and strategic planning to secure vital components for successful projects.
UK Rooftop Market Analysis To 2030
Almost all of the rooftop segments are in high-growth mode today, some more so than others. The only subsegment that is awaiting a rocket booster is the retrofit residential segment – the part of the UK solar industry that propelled initial growth in the sector back in 2010 when Feed-in Tariffs (FiTs)¹ were first introduced.
In the graph below, the bars split out the segments into residential and different rooftop-size bands reflecting the various drivers.
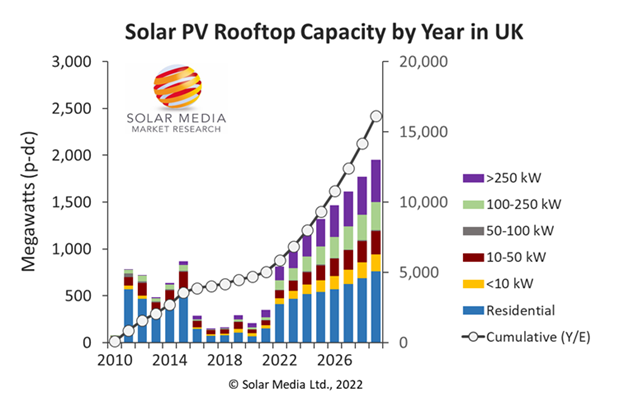
The graph above indicates that 10.3 gigawatts (GW) of new rooftop capacity are set to be installed, with 4.2 GW allocated for residential use and 6.1 GW for commercial and industrial purposes. Local councils, Members of Parliament (MPs), government departments, and the general public support rooftop solar PV systems, driving investment and advocating for the expansion of solar panel installations.
The rooftop PV market is characterized by a high level of deployment certainty and minimal risk.
The Surge of Residential Solar Installations in the UK

The residential sector in the United Kingdom has been experiencing growth and widespread acceptance across all regions. This trend is expected to contribute to the market’s expansion throughout the projection period.
In 2022, small-scale residential solar panel installations accounted for a significant 73% of the UK’s newly added solar capacity, as reported by Energy Live News. Residential solar panel installations nearly doubled compared to the previous year, 2021. Solar Energy UK Chief Executive Chris Hewett emphasized that to meet government targets, residential solar panel installations will need to continue doubling each year.
The significant rise in small-scale solar photovoltaic (PV) installations can be credited to a combination of soaring electricity prices and the declining costs of PV panels and batteries. In June 2022, a noteworthy milestone was achieved, marking the first time since March 2016 that domestic installations accounted for over a quarter (26%) of the UK’s overall solar capacity.
Commercial Buildings Impact On The UK Solar Market

A recently published statement by the UK government’s newly formed solar task force’s inaugural meeting emphasized the untapped potential of commercial sites for solar energy utilization. Schools, warehouses, and car parks emerged as crucial players in democratizing affordable solar power.
The task force’s strategies to enhance solar capacity include a 2024 solar roadmap release, expanding the solar workforce, and identifying opportunities to strengthen global supply chains and promote innovation.
Experts predict sustained growth in the UK’s commercial solar industry over the next decade, with solar energy potentially constituting up to 20% of the country’s total electricity generation by 2030. The government provides financial incentives like the Solar Investment Allowance and the Smart Export Guarantee to incentivize solar panel adoption among businesses. The government’s commitment to investing in renewable energy, including solar power, is expected to drive further commercial solar adoption.
The future of commercial solar in the UK appears promising, bolstered by declining costs, government support, and rising demand for clean energy.
Ground-Mount Solar Market Analysis
The UK’s ground-mounted solar energy sector has been the primary contributor (63%) to the goal of reaching 15.8 GW of cumulative capacity by the end of 2022. This trend is expected to continue, with an estimated 60% contribution by the end of 2029.
Segmenting ground-mounted capacity by site size is the most effective approach. Solar farms dominate existing and upcoming capacity rather than small arrays in backyards.

Essentially, there are two sub-segments in utility ground-mounted solar:
- Sites up to 50 MWac (Megawatt alternating current; no longer peak-dc defined): This sub-segment includes utility ground-mounted solar sites with a capacity of up to 50 MWac. These sites are subject to certain criteria and regulations.
- ‘Larger’ sites requiring government approval: This sub-segment refers to utility ground-mounted solar sites that are larger than 50 MWac, and their development requires approval from national or devolved government departments. The specific threshold criteria for approval may vary depending on the department in question.
Over the years, utility solar farm sizes in the UK have evolved. Initially, sites were mostly 5 MW, driven by FiT limits. When Renewables Obligation Certificates (ROCs)2 came into play, sites in the 30-50 MW range became common, limited by the 50 Megawatt peak-direct current (MWp-dc) cap at the National Grid planning stage.
In 2022, there was a growing interest in 5-20 MW sites, primarily from public-sector and landowner investments. However, over 95% of current and future capacity follows a more structured cash-flow process (and asset-owned) driving solar farm development at 50 MW and higher levels.
Looking ahead to 2030, predicting ground-mounted solar deployment carries some risks such as public opinion and political divide, changes in land use, and increased objections due to concerns, including environmental impact and public perception and acceptance. Nevertheless, experts predict that despite potential obstacles, substantial growth in large-scale solar farms will likely occur in the next seven years.
Conclusion
To sum it up, the United Kingdom’s solar market is heading in a promising direction towards a more environmentally friendly and sustainable future. The surge in residential solar adoption, influenced by increasing energy expenses, is notable, and non-residential properties offer substantial potential for solar energy generation.
Finally, ground-mounted solar, a cornerstone of the UK’s renewable energy aspirations, is poised for significant expansion, and the nation is unwavering in its dedication to a cleaner, solar-powered future.
Learn more about the renewable energy sector in our blogs, newsletters, and industry news!
¹Feed-in Tariffs are government incentives that offer guaranteed payments above market rates to encourage the use of renewable energy and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
2 ROCs were certificates given to renewable energy generators in the UK for each megawatt-hour of clean electricity produced, which could be sold to meet renewable energy obligations.

