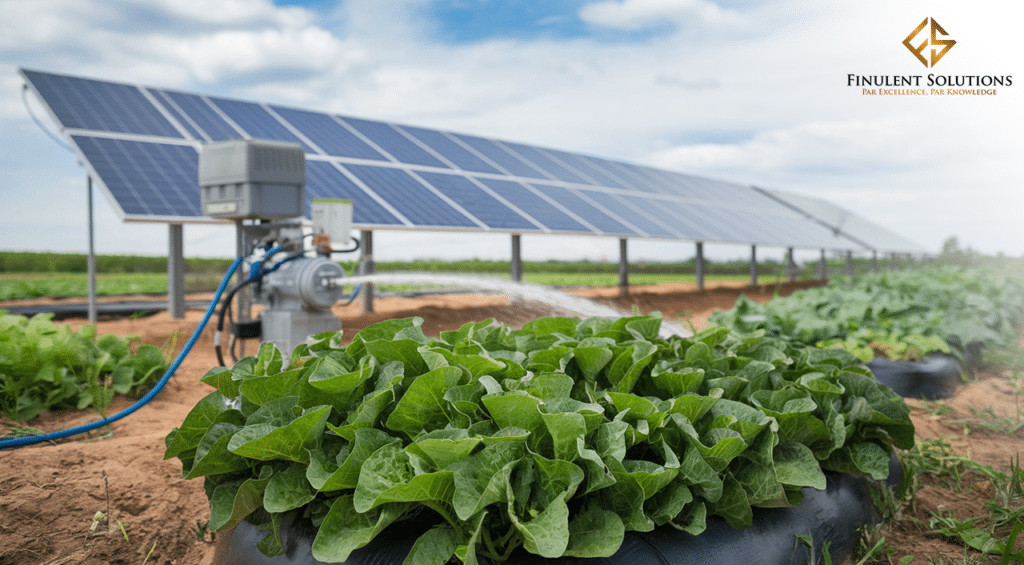
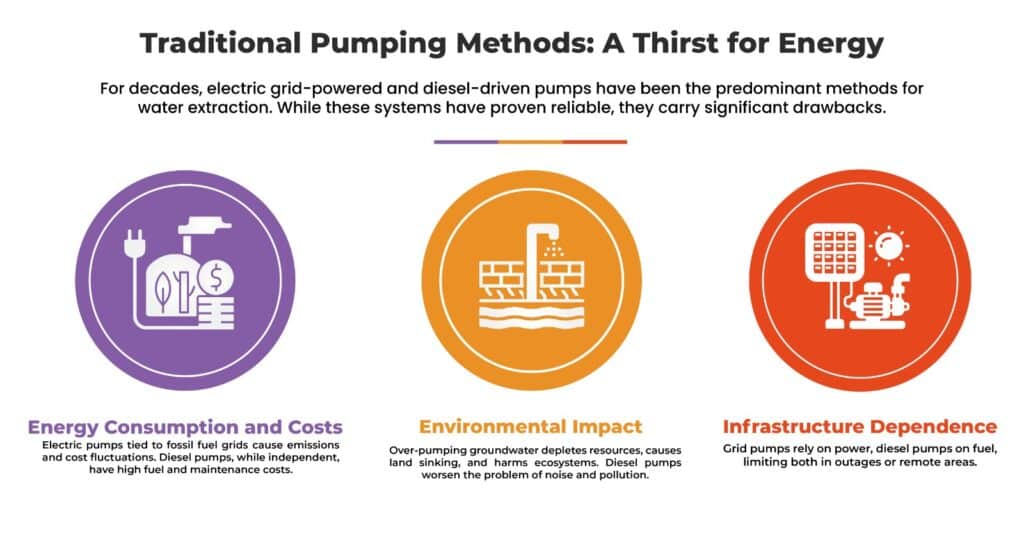
Water, a cornerstone of life, is a finite resource that faces increasing pressure due to population growth, urbanization, and climate change. Equitably allocating water and utilizing it sustainably is a major challenge for the contemporary world. Although water demands have been addressed through traditional methods of pumping, there are often times when these capacities are limited concerning efficiency, energy consumption, and environmental footprints. It is important to understand the issues associated with equitable water distribution and how solar energy- powered pumping technology can help in addressing them.
Solar Energy-Powered Pumping Solutions: A Sustainable Alternative
Solar-powered pumping systems offer a compelling solution to the challenges posed by traditional methods. By harnessing the sun’s energy, these systems provide a clean, renewable, and cost-effective approach to water management.
Types of Solar Pumps
It is necessary to contemplate well depth, water volume, and the actual application for optimal solar pump selection. Common types include:
- Submersible Solar Pumps: These pumps are directly installed in the well and hence useful for deep wells or with high-pressure requirements.
- Surface-Mounted Solar Pumps: These are surface-mounted solar pumps that are submerged in wells, and mostly used for irrigation & livestock watering from shallow wells.
- Solar-Powered Centrifugal Pumps: High-volume demands? Solar-powered centrifugal pumps are the solution for large-scale applications.
- Solar-Powered Piston Pumps: Best suited for deep wells with low flow rates, these pumps offer reliability and durability.
System Design and Installation
Effective solar pumping system design involves careful consideration of several factors:
- Solar Panel Capacity: Accurate estimation of water demand is crucial for determining the optimal solar panel size to meet energy requirements.
- Pump Selection: The pump’s performance curve should align with the system’s flow rate and head requirements.
- Energy Storage: Batteries can be integrated to store excess solar energy for use during periods of low sunlight.
- Inverter: A solar inverter converts the DC power from the panels into AC power for the pump.
- Pump Controller: This component optimizes pump operation based on solar radiation and water demand.
Case Studies: Real-World Benefits
Solar Energy- powered pumping systems have proven to be transformative across various sectors.
- Agriculture: Solar pumps have revolutionised Indian agriculture, empowering millions with clean, renewable energy. For instance, in Tamil Nadu, solar-powered irrigation has enabled farmers to grow sugar cane and rice (two water-intensive crops) more sustainably.
- Community Water Supply: Solar pumps have brought drinking water to thousands of rural African communities – significantly lightening the load for women & children. For instance, the use of solar pumps in Kenya has increased safe water access and reduced the prevalence of water-borne diseases.
- Industrial Applications: Mining operations in remote areas have adopted solar pumps to reduce diesel consumption and lower operational costs. For instance, a gold mine in South Africa has switched to solar power for pumping water out of the pits and it has resulted in cost savings as well as lower carbon emissions.
Future Trends: Expanding the Potential of Pumping with Solar Energy
The advent of solar pumping will continue to grow for the better and we look forward with optimism as these developments in solar technology coupled with pump design come into play:
- Higher Efficiency Solar Panels: As panel efficiency increases, pumps will be able to work more effectively and at a higher capacity for lower cost.
- Smart Pump Controllers: With the help of improved controllers one can optimize water delivery and energy usage by adjusting pump operations.
- Hybrid Systems: Integration into other renewable energy sources will provide a more reliable system with improved performance.
- IoT Integration: Remote monitoring and control of solar pumping systems will enable proactive maintenance and troubleshooting.
Conclusion:
Water and energy are inextricably linked thus water-energy nexus becomes a top priority concern issue for companies. Solar energy offers a compelling solution to optimize both resources. By harnessing the sun’s power, enterprises can significantly reduce water consumption, curtail energy expenses, and enhance their environmental footprint.
From heating water to firing pumps and treatment processes, solar covers a lot of ground in the toolkit for providing clean water. Its application spans a variety of industries including agriculture, manufacturing, and data centers, demonstrating its wide-reaching capabilities.
Adoption of solar water grading is not only the need to make this environment friendly; rather a very wise business decision. The money saved is quite significant as it helps in mitigating the operation cost and risk. In addition, it paints businesses in a positive light as leaders of sustainability and also attracts eco-friendly patrons towards them.
To fully realize the advantages of solar water optimization, a comprehensive approach is essential. This includes conducting thorough assessments, selecting appropriate technologies, and implementing effective monitoring systems. By investing in solar energy and water conservation, businesses can secure a more sustainable, resilient, and profitable future.

