The International Energy Agency’s latest report, titled ‘World Energy Investment 2023,’ reveals a significant increase in clean energy investment in recent years, primarily driven by Electric Vehicles (EVs) and renewable power. However, this surge in investment is primarily concentrated in advanced economies and China. Additionally, the report highlights a concerning trend of a slight reversal in the decline of clean energy technology prices over the past two years.
The report attributes the increase in clean energy investment to the economic recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic and global efforts to address energy scarcity. Comparing the International Energy Agency’s 2023 forecasts with actual data from 2021, the report shows that annual investments in green energy have surpassed those in fossil fuels, experiencing a growth rate of 24% compared to 15% during this period.
Recent geopolitical events have also had a notable impact on the energy market. Specifically, the report points out that Russia’s invasion of Ukraine has caused substantial instability in the fossil fuel markets. Surprisingly, this volatility has unintentionally accelerated the deployment of various renewable energy technologies, despite triggering an immediate scramble for oil and gas resources.
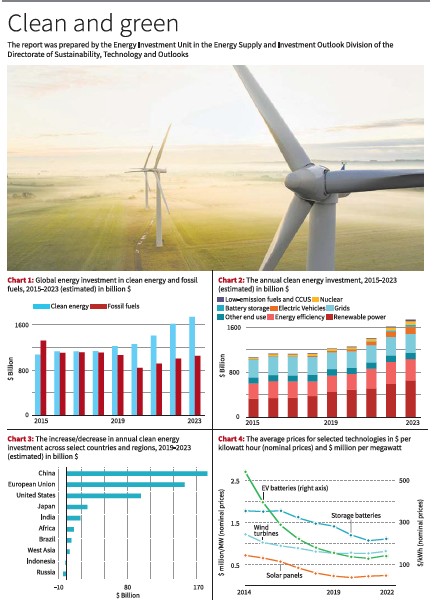
Chart 1 in the report visualizes the global energy investment in clean energy and fossil fuels from 2015 to 2023, estimated at billion dollars. It demonstrates that while investments in fossil fuels have remained stagnant, there has been a significant increase in the flow of funds into clean energy in recent years. The report attributes this shift towards greener fuels primarily to the dominance of renewable power and EVs, supported by contributions from other areas such as battery technology, heat pumps, and nuclear power.
In 2023, it is expected that nearly 90% of the total investment in electricity generation will be directed towards low-emission power sources. Among these sources, solar energy is projected to be the most prominent. Investment in solar energy is estimated to exceed $1 billion per day in 2023, totaling $380 billion for the year. Chart 2 presents the annual clean energy investment from 2015 to 2023, also estimated at billion dollars.
The report reveals that over 90% of the surge in clean energy investment since 2021 has been concentrated in advanced economies and China. The rise in clean energy investment within these regions has outpaced the combined total of clean energy investment in the rest of the world.
While advanced economies and China are leading the way, other regions are also progressing. India, for example, continues to demonstrate robust investment in solar energy. Brazil’s deployment of renewable energy is consistently on an upward trajectory, and investor interest is growing in parts of West Asia, particularly in Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Oman. However, the report argues that despite these positive developments, many countries still face hurdles. Factors such as higher interest rates, ambiguous policy frameworks, market designs, financially constrained utilities, and a high cost of capital are impeding investment. Chart 3 illustrates the annual clean energy investment increase across select countries and regions from 2019 to 2023, estimated in billion dollars.
In a departure from the previous trend of cost reductions, the prices of several critical clean energy technologies experienced an increase in 2021 and 2022. This rise can be attributed to escalating input prices for essential minerals, semiconductors, and bulk materials like steel and cement. Chart 4 provides an overview of the average prices for selected technologies, expressed in dollars per kilowatt hour (nominal prices) and dollars per megawatt million.
Source: The Hindu

